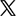Have you ever wondered how your favorite songs and podcasts are converted into digital files that can be played on your device? This is where audio codecs come in! From streaming music to downloading podcasts, audio codecs are essential to our everyday audio experiences. In this article, we'll explain what audio codecs are, how they work, and why they're important, even if you're not a tech expert.

1. What is an Audio Codec
An audio codec works like a translator for sound. It converts sounds we hear in the real world into digital data that can be saved and played back on computers, phones, and other devices. The term refers to how audio data is transformed for efficient storage, transmission, and playback. It is an essential component of the digital world, allowing for the compression and decompression of audio data. This procedure helps in the reduction of file sizes while preserving sound quality.
An audio codec is a technology that compresses and decompresses audio data before transmitting or storing it. The term "codec" is a combination of "coder" and "decoder," referring to the two basic functions of an audio codec. Simply put, it compresses audio data for economical transmission or storage while also allowing it to be decoded for playback.
2. How Audio Codecs Work
Audio codecs compress audio data with the help of unique algorithms. This compression reduces the size of audio recordings, making them easier to keep and send via the Internet. When you play the audio back, the codec decodes the compressed data and converts it into a sound that can be heard. To further grasp how audio codecs work, we'll look at the encoding and decoding processes. When you listen to digital audio, it is compressed to reduce file size. There are two forms of compression: lossless and lossy.
- Lossy Codecs: Lossy codecs, like MP3 and AAC, discard some audio data to achieve high compression ratios, resulting in smaller file sizes. They are commonly used for digital music streaming, internet telephony, and audio file compression. These codecs achieve great compression levels, making them ideal for streaming or limited storage space. However, some audio quality is lost in the process.
- Lossless Codecs: Lossless codecs like FLAC and ALAC compress audio data without sacrificing any information, preserving the original audio quality. They are favored for archiving music libraries and professional audio production.This ensures that the audio quality is not lost during compression. Lossless codecs are often employed in applications that need high audio fidelity, such as professional music creation and archiving.

3. Popular Audio Codecs
There are numerous audio codecs available, but some of the most popular include MP3, AAC, and FLAC, which use various compression techniques to optimize audio data for storage and transmission. Their purpose is to make digital audio processing easier for non-audiophiles, and they play an important role in defining audio quality perceptions. Each codec has its own method of compressing audio data and varying levels of quality. For example, MP3 is frequently used for music since it can significantly reduce file size while keeping acceptable quality. FLAC, on the other hand, is a lossless codec, which means it keeps the original sound quality while causing no data loss.
- 1. MP3 (MPEG-1 Audio Layer III): MP3 is one of the most recognizable audio codecs. It offers good compression while maintaining acceptable audio quality. MP3 is commonly used for music streaming and portable audio players.
- 2. AAC (Advanced Audio Coding): AAC is known for its superior audio quality at lower bitrates. It is widely used in applications like iTunes and YouTube, offering a good balance between quality and file size.
- 3. FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Codec): FLAC is a popular lossless codec, providing full audio fidelity without any loss in quality. It's commonly used in music production, audiophile collections, and digital archiving.

4. Factors Affecting Audio Codec Choice
Some people worry that using audio codecs could affect the quality of their music, but in actuality, many modern codecs are designed to preserve as much of the original sound as possible. They use advanced tactics based on how our ears hear sound to delete sections of the audio that we won't notice are absent. This is known as perceptual coding, and it allows for high-quality music recordings to be stored in small amounts of space.
When selecting an audio codec, there are many factors to consider. These include the required sound quality, file size, and compatibility with various devices and software. For example, if you want to play music online, you could use a codec such as AAC, which provides high quality at lower bitrates, resulting in reduced file sizes.
Audio Quality: Consider the level of audio fidelity required for the intended use. Lossless codecs like FLAC are best for maintaining original audio quality, while lossy codecs like MP3 or AAC achieve a balance between quality and file size.
File Size: Assess the available storage or bandwidth limitations. Lossy codecs excel at lowering file size, making them ideal for streaming or restricted storage devices.
Compatibility: To ensure playback compatibility, make sure the codec you choose is widely supported across all devices and systems.

5. Future Trends in Audio Codecs
Audio codecs are used in many different industries and applications. For example, in music streaming services like Spotify or Apple Music, codecs are used to deliver high-quality audio over the internet while keeping data usage and buffering times low. In video production, codecs are used to compress audio tracks alongside video to create smaller files that are easier to work with and share.
As technology advances, we should expect much more progress in audio codecs. New codecs are always being developed to provide improved sound quality at lower bitrates, which results in smaller file sizes. There is also a growing interest in immersive audio formats like Dolby Atmos and Sony 360 Reality Audio, which use advanced codecs to create a more immersive listening experience. These developments are intended to improve audio quality, increase compression efficiency, and accommodate new audio formats. Some of the trends are:
- 1. Object-Based Audio Codecs: These codecs enable immersive audio experiences by treating individual audio elements as separate objects, allowing for customized audio playback.
- 2. High-Resolution Audio Codecs: With the increasing availability of high-quality audio playback devices, codecs that can handle higher sample rates and bit depths are becoming more prevalent.

6. How to Convert Audio Format
Best for: Beginners, music collectors, and DVD owners. People looking for a simple, reliable, and powerful audio converter for everyday use, resolving incompatible format issues, and archiving or sharing audio files.
Not for: Linux users trying to find a free audio converter for the Linux system.
What if you want to convert an audio format to another? VideoProc Converter AI is an ultimate tool for audio converting, video converting, video downloading, and video editing. It can convert practically any video or audio file, including AAX, WAV, MP3, FLAC, M4A, AIFF, M4R, AAC, AC3, OGG, and more. Also, the conversion speed is 47 times faster than usual audio conversion or video conversion software due to the hardware level-3 acceleration technology.

VideoProc Converter AI - Convert Audio Formats Easily
- Supports removing noise from video with Audio AI feature.
- Quality-oriented conversion for 420+ codecs and formats.
- Fast conversion speed with GPU acceleration.
- Serves as a video compressor, free downloader, and screen recorder as well.
Step 1: Run VideoProc Converter AI and click on the Video Converter section from the main page.
Step 2: Click +Music to import your audio files. You can just drag and drop your files here. Choose your target format and click the RUN button to begin.
Step 3: Then your files will be converted to another format immediately. You can set it to shut down your computer or open the output folder after the conversion is completed.
Conclusion
Audio codecs play an important role in our digital life, whether we recognize it or not. Codecs work behind the scenes to deliver high-quality audio to our ears if we're streaming music or watching videos on our smartphones. Understanding how audio codecs function and the elements that influence their performance allows us to make more informed decisions about storing, sharing, and enjoying our favorite audio files.