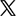Back in the day, if you used camcorders and inserted the card into your computer, you might remember encountering AVCHD folders with complicated directories. Sifting through these folders, you will eventually find your videos.
However, there was always the worry of disrupting the folder structure and facing playback errors. So, what exactly is AVCHD? How should you handle this video format correctly? And how can you convert AVCHD to the more commonly used MP4 format? We've got all the detailed information and a step-by-step tutorial for you below.
Part 1. What Is AVCHD Codec
AVCHD, standing for Advanced Video Coding High Definition, is a format used for recording and playing back high-definition video digitally. Created by Sony and Panasonic, it debuted in 2006 for high-definition consumer camcorders and was eventually adapted for professional applications.
Below is a quick glance at AVCHD format basics.
Resolutions: AVCHD supports a range of video resolutions, including standard, high-definition, and stereoscopic (3D).
Video Compression: The format uses the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC compression standard.
Audio Compression: It supports Dolby AC-3 (Dolby Digital) and uncompressed linear PCM audio.
Use Cases: AVCHD can be recorded onto DVDs, memory cards, solid-state drives, and hard disk drives.
Playback Compatibility: This format is compatible with Blu-ray players and allows recordings to be transferred to computers for editing and playback.
Professional Variants: AVCCAM & NXCAM and AVCHD progression. The former are professional variants of AVCHD used by Panasonic and Sony, respectively; the latter is an extension of the format to include 1080-line 50fps and 60fps modes, as well as stereoscopic video.
Part 2. How to Open AVCHD Codec Format
You may find AVCHD file format in DVDs, memory cards, or folders already ripped and shared by someone else. To open the AVCHD file format, you can drag and drop the file to the supported media player, such as a free open-source VLC player, GOM player, 5K player, or KMPlayer.
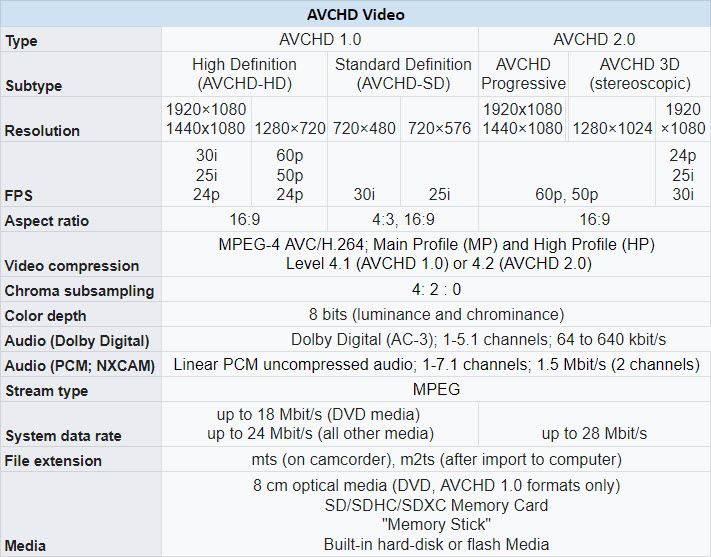
If you want to edit an AVCHD file, you can use VideoProc Converter AI. It is an all-in-one video editor and converter, with AI-powered tools to enhance video quality.

Given that some AVCHD files are old footage from legacy camcorders, it is common to find 720p or 480p low-resolution old videos. The Super Resolution tool in VideoProc Converter AI can help you easily upscale and sharpen the video with AI algorithms.

VideoProc Converter – Best Video Processing Tool for AVCHD Videos
- Convert AVCHD to MP4 (h264/mts/m2ts from Sony, Samsung, Panasonic camcorders).
- Merge chopped-up clips (mts/m2ts/ts files) in AVCHD/BDMV folders into a single video.
- Analyze non-standard AVCHD formats/DVD/camcorder files and convert to MP4/MOV.
- Toolbox to convert, edit, record, download video, copy DVD, deinterlace video.
- New: AI models to upscale and enhance videos, old footage, and images to 4K with details.
![]() Excellent
Excellent ![]()
Part 3. AVCHD vs MP4: Which One Should I Use
Now that we've covered the basics about AVCHD format, how does it compare to MP4? In fact, MP4 is merely a container format that wraps video streams, audio streams, and other metadata. So the real question may be, how does AVCHD compare with H264, H265, and other MP4-supported video codecs?
Since H264 is one of the most compatible codecs commonly seen in MP4 containers, we will compare AVCHD with H264.
1. Compression and Quality
H264 (AVC): Known for its excellent compression efficiency, H264 can deliver high-quality video at lower bit rates. It achieves this through advanced features like motion compensation, variable block-size segmentation, and multi-picture prediction. This means you get high-quality video without using too much storage space, making it ideal for streaming, web use, and storage.
AVCHD: While AVCHD also offers good compression, it doesn't match the efficiency of H264. AVCHD was designed to maintain high video quality, especially for camcorder recordings in the 20th century.
2. Compatibility and Playback
H264: Almost universally supported across devices and platforms. You can play H264 files on smartphones, tablets, computers, smart TVs, and many other devices.
AVCHD: While widely supported, AVCHD files are primarily geared towards playback on specific devices like Blu-ray players, certain camcorders, and compatible media players. Playback on other devices might require conversion.
3. Use Cases
Streaming and Online Content: H264 wins. Due to its high compression efficiency and widespread support, H264 is the preferred choice for online video platforms like YouTube, Vimeo, and streaming services like Netflix and Hulu.
Editing and Post-Production: If you're planning to edit your videos or use them in post-production, H264's compatibility with most editing software makes it a convenient choice. As for AVCHD, many professional editing suites support this file format, but the files can be larger and more cumbersome to work with, especially for extensive editing projects.
DVD and Blu-ray: AVCHD files can be easily burned to DVD and Blu-ray discs for playback on compatible players, making it a good choice for creating physical copies of your videos.
Wrap Up
To playback AVCHD files, you can use VLC media player, KMPlayer and the alike, To better preserve your AVCHD files, you can use VideoProc Converter AI to 1:1 copy the file to H264 MP4 format. MP4 is more widely supported for social sharing, video editing, and cross platform playback.
Free Download VideoProc Converter AI as the must-have video toolkit: